TN TBI Service Coordination Program: There are currently eight Service Coordinators located in various agencies across the state providing assistance to people with brain injury and family members. Services are free of charge.
TN TBI Service Coordination Program: There are currently eight Service Coordinators located in various agencies across the state providing assistance to people with brain injury and family members. Services are free of charge.
Family Voices of TN (FVTN): Family Voices connects families with each other, community resources, experienced parent mentors, tools to navigate complex systems in healthcare and insurance and more.Serves families and children across all diagnoses and all ages. Call or email: 615-383-9442 familyvoices@tndisability.org
TN Respite Coalition: The Tennessee Respite Coalition's Mission is to enhance the quality of life for family caregivers through respite. They provide resources that enable caregivers to reclaim a little piece of themselves and restore balance to their lives and relationships. FAQs 615-269-8687.
TN Information on Respite Providers or Programs: This resource will help to navigate Finding Respite Providers & Programs and Funding Eligibility resources.
TN Lifespan Respite Program is funded by the Administration for Community Living, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, State Lifespan Respite Programs or Projects are run by a designated state government lead agency, which works in collaboration with a state respite coalition and an Aging and Disability Resource Center Program/No Wrong Door System. Their purpose is to implement statewide systems of coordinated, community-based respite for family caregivers caring for individuals with special needs of all ages. To learn more contact a consultant at the Tennessee Commission on Aging and Disability. 615-253-3680.

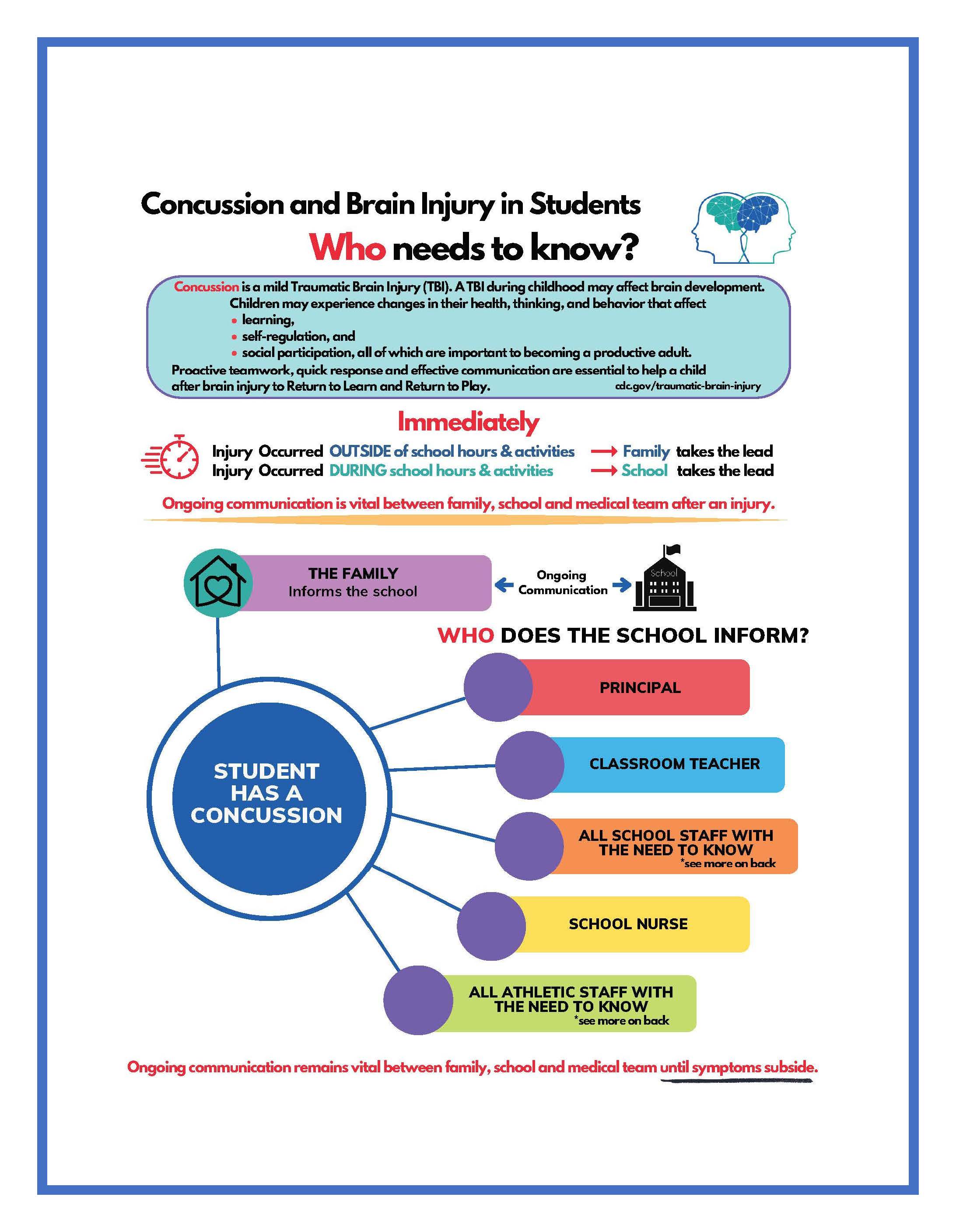
Concussion and Brain Injury in Students, Who needs to know? Concussion is a mild Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI). A TBI during childhood may affect brain development. Children may experience changes in their health, thinking, and behavior that affect learning, self-regulation, and social participation, all of which are important to becoming a productive adult. Proactive teamwork, quick response and effective communication are essential to help a child after brain injury to Return to Learn and Return to Play. cdc.gov/traumatic-brain-injury Word Document File
 Go Back to Play After a Concussion: This is a concussion return to play manual created for student-athletes who do not have access to an athletic trainer to guide them through the Return To Learn (RTL) process. This manual follows the RTP process required by the Tennessee state concussion law. This resource is a way for parents or coaches to track and document the progress of their athletes. Vanderbilt Sports Concussion Center
Go Back to Play After a Concussion: This is a concussion return to play manual created for student-athletes who do not have access to an athletic trainer to guide them through the Return To Learn (RTL) process. This manual follows the RTP process required by the Tennessee state concussion law. This resource is a way for parents or coaches to track and document the progress of their athletes. Vanderbilt Sports Concussion Center
A Guide to Possible Changes After Brain Injury: For Young Children Ages 7 and Under. Text Version.
 A Guide to Possible Changes After Brain Injury: For School-Aged Children and Adults. By design, the Guide is best when distributed by rehabilitation personnel in inpatient and outpatient therapy programs and by medical personnel in trauma units, pediatrician’s offices, family practices, neurology offices, surgical offices, and other specialty offices. It is meant to be given to anyone who has sustained a diagnosed brain injury, as well as anyone who sustained a significant trauma where they may experience brain injury symptoms and downstream consequences; even if they do not show early symptoms or early symptoms seem to have cleared. English and in Español
A Guide to Possible Changes After Brain Injury: For School-Aged Children and Adults. By design, the Guide is best when distributed by rehabilitation personnel in inpatient and outpatient therapy programs and by medical personnel in trauma units, pediatrician’s offices, family practices, neurology offices, surgical offices, and other specialty offices. It is meant to be given to anyone who has sustained a diagnosed brain injury, as well as anyone who sustained a significant trauma where they may experience brain injury symptoms and downstream consequences; even if they do not show early symptoms or early symptoms seem to have cleared. English and in Español
 TBI in the Youth Justice System Infographic
TBI in the Youth Justice System Infographic
 Children's Safety Network: Traumatic Brain Injury Resource Guide
Children's Safety Network: Traumatic Brain Injury Resource Guide

Brainline Kids: Children with TBI. Information and resources for families and educators. A concussion is a blow or jolt to the head that can change the way your brain normally works. Also called a mild traumatic brain injury, a concussion can result from a car crash, a sports injury, or from a seemingly innocuous fall. Concussion recovery times can vary greatly. Most people who sustain a concussion or mild TBI are back to normal by three months or sooner. But others have long-term problems remembering things and concentration. Accidents can be so minor that neither doctor nor patient makes the connection.
Concussion in Kids: Children with a brain injury can have the same symptoms as adults, but it’s often harder for them to share how they feel.
Moderate to Severe TBI: Guidance on how to help children with moderate or severe brain injuries through rehabilitation and recovery.
Raising a Child with TBI: Raising a child with TBI can be a daunting job. How can you give your child the help that he or she needs while still maintaining some semblance of a normal life?
School and Education: Whether a student with traumatic brain injury is in elementary school or in college, transitioning back to school post-injury can be difficult on many levels.
Teens with TBI: Adolescence is a tough enough time. What happens when a brain injury is added to the mix?
Sports Concussions: Concussions are a widely recognized sports injury, but they are more common—and subtle—than people might think.


Traumatic Brain Injury: A Guide for Caregivers of Service Members and Veterans: This guide is a recovery support tool to assist caregivers of service members and veterans who have sustained a traumatic brain injury at any severity level. This 2021 revision replaces the original guide released in 2010.
Topics include:
- Understanding TBI: This section includes information on types and diagnosis of TBI, the health care team, and what the recovery process may look like.
- Caregiver Strategies for Managing the Effects of TBI: This section includes information about understanding and addressing the different symptoms of TBI for the caregiver.
- Becoming a Family Caregiver: This section covers starting the caregiver journey, becoming an advocate, and learning how to take care of oneself.
- Caregiver Resources: This section includes helpful links for caregivers, printable forms and a glossary.

 University of Alabama at Birmingham TBI Model Systems (UAB TBIMS):
University of Alabama at Birmingham TBI Model Systems (UAB TBIMS):
TBI Factsheets: The UAB-TBIMS offers a series of Information Sheets developed through a collaboration between the Model Systems Knowledge Translation Center (MSKTC) and the TBI Model Systems of Care. These fact sheets are written for consumers. All Infosheets are free to print and disseminate for educational purposes.
Rehab Tip Sheets: These tip sheets offer rehabilitation care providers and consumer caregivers step-by-step instructions and photo illustration on performing common activities.
- Wheelchair Positioning (PDF)
- Assisted Pressure Relief (PDF)
- Lift Transfers of Patients (PDF)
- Assisted Transfers of Patients (PDF)
- Swallowing Strategies (PDF)
- Walking following Brain Injury (PDF)
- Managing Irritability and Temper Following Brain Injury (PDF)
- Resting Hand Splint Application (PDF)
- Bed Positioning for the Immobile Patients (PDF)

National Academy for State Health Policy (NASHP): NASHP Report: What Family Caregivers Need: Findings from Listening Sessions
- A new report released this week by the National Academy for State Health Policy (NASHP) shares information collected from family caregiver listening sessions. The listening sessions were designed to provide multiple forums for family caregivers to share their challenges and needs, and recommendations for services, supports, and policies to address these needs. This report, which was written by the University of Massachusetts at Boston and Community Catalyst, is a component of the Recognize, Assist, Inform, Support, and Engage (RAISE) Family Caregivers Act of 2017, and is part of ACL’s work to implement the Act.
- The family caregiver listening sessions included a range of diverse caregivers, from teen caregivers to grandparents providing care, and caregivers of varying racial and ethnic backgrounds. The listening sessions directly captured the emotional and financial stresses caregivers experience, and their priorities and concerns, including respite, caregiving education and training, and financial considerations, including direct pay for caregiving, workplace flexibility, and tax policy changes that support caregivers.
Visit the RAISE Act Family Caregiver Resource and Dissemination Center to read the report.
Brain Injury Definitions
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): CDC defines a traumatic brain injury (TBI) as a disruption in the normal function of the brain that can be caused by a bump, blow, or jolt to the head, or penetrating head injury. Everyone is at risk for a TBI, especially children and older adults.
Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA): The Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) is a law that makes available a free appropriate public education to eligible children with disabilities throughout the nation and ensures special education and related services to those children. Resources for Parents and Families.
TN Department of Education TBI Evaluation Guidance, Revised 2018